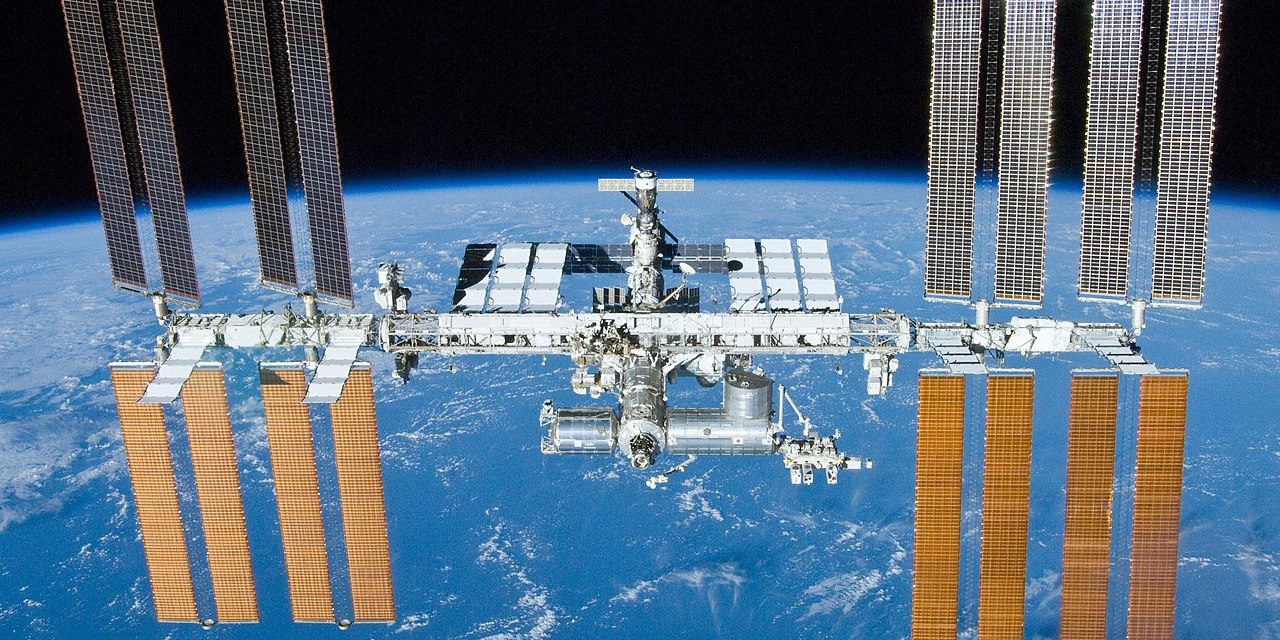
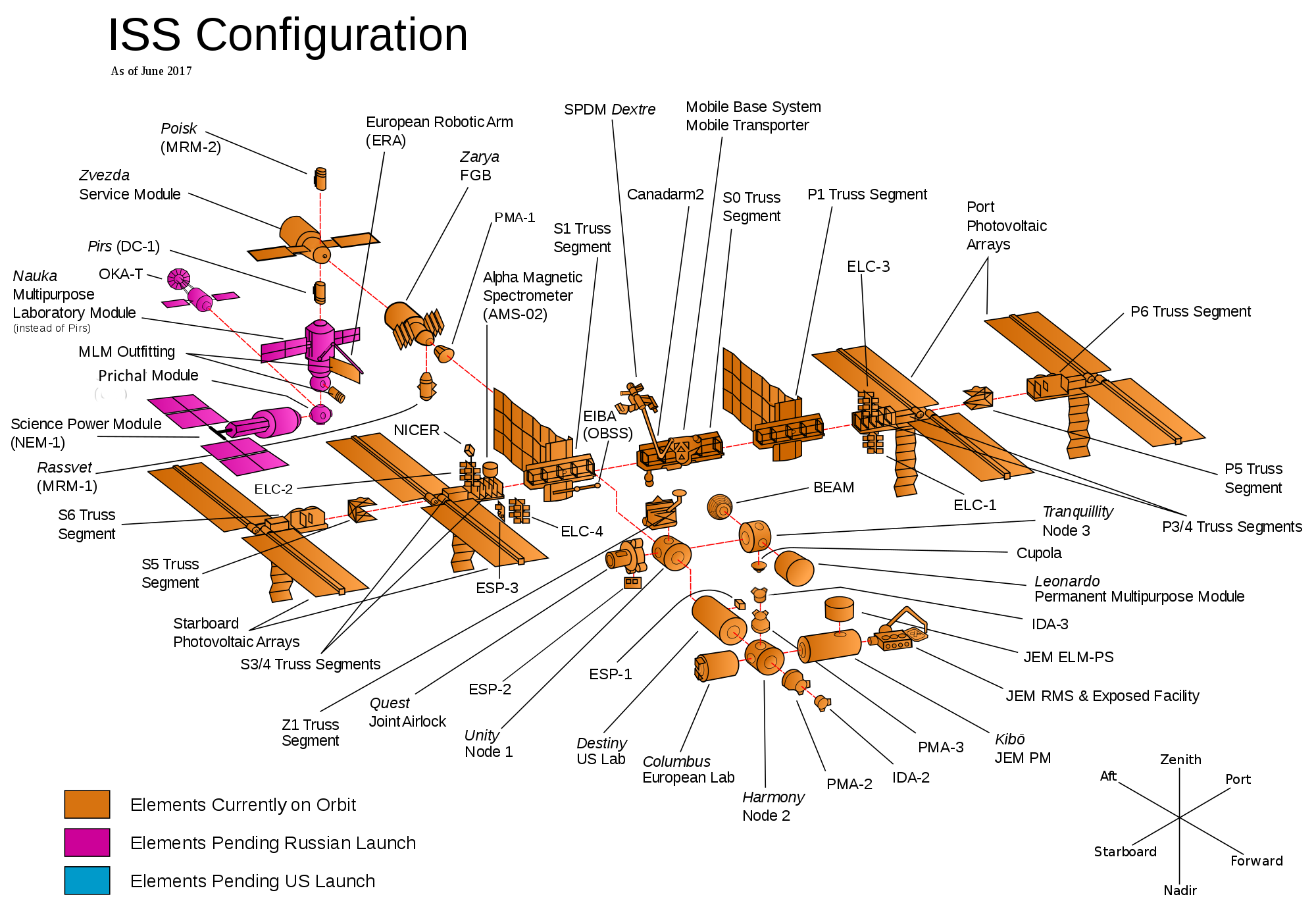
The International Space Station (ISS) is a space station (habitable artificial satellite) in low Earth orbit. The ISS programme is a joint project between five participating space agencies: NASA (United States), Roscosmos (Russia), JAXA (Japan), ESA (Europe), and CSA (Canada). The ownership and use of the space station is established by intergovernmental treaties and agreements. The ISS serves as a microgravity and space environment research laboratory in which crew members conduct experiments in biology, human biology, physics, astronomy, meteorology, and other fields. The station is suited for the testing of spacecraft systems and equipment required for missions to the Moon and Mars. The ISS maintains an orbit with an average altitude of 400 kilometres (250 mi) by means of reboost manoeuvres using the engines of the Zvezda module or visiting spacecraft. It circles the Earth in roughly 92 minutes and completes 15.5 orbits per day.

How to Spot the Space Station
Did you know that if you look really carefully at the Sky you can spot the International Space Station? Those videos from NASA can give you some useful hints.
E-BOOKS about the space station
Did you know people live and work in laboratories in space? How are these space stations built? Find out more in Space Stations.
What’s longer than a football field, weighs more than 450 cars, yet flies miles above Earth’s surface? It’s the International Space Station. In this book, you’ll learn how the station was built and how crew members live and work there